024 38560777
Hexadecimal (Hex) (Hệ cơ số mười sáu)
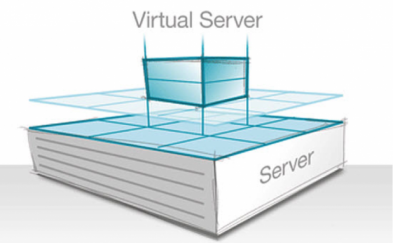
Trong toán học và trong khoa học điện toán, hệ thập lục phân (hay hệ đếm cơ số 16, tiếng Anh: hexadecimal), hoặc chỉ đơn thuần gọi là thập lục, là một hệ đếm có 16 ký tự, từ 0 đến 9 và A đến F (chữ hoa và chữ thường như nhau). Hệ thống thập lục phân hiện dùng, được công ty IBM giới thiệu với thế giới điện toán vào năm 1963. Một phiên bản cũ của hệ thống này, dùng các con số từ 0 đến 9, và các con chữ U đến Z, đã được sử dụng trong máy tính Bendix G-15, ra mắt năm 1956.
Ví dụ, số thập phân 79, với biểu thị nhị phân là 01001111, có thể được viết thành 4F trong hệ thập lục phân (4 = 0100, F = 1111).
By English
In mathematics and computer science, hexadecimal (also base 16, or hex) is a positional numeral system with a radix, or base, of 16. It uses sixteen distinct symbols, most often the symbols 0–9 to represent values zero to nine, and A, B, C, D, E, F (or alternatively a–f) to represent values ten to fifteen. For example, the hexadecimal number 2AF3 is equal, in decimal, to (2 × 163) + (10 × 162) + (15 × 161) + (3
Each hexadecimal digit represents four binary digits (bits), and the primary use of hexadecimal notation is a human-friendly representation of binary-coded values in computing and digital electronics. One hexadecimal digit represents a nibble, which is half of an octet or byte (8 bits). For example, byte values can range from 0 to 255 (decimal), but may be more conveniently represented as two hexadecimal digits in the range 00 to FF. Hexadecimal is also commonly used to represent computer memory addresses. × 160), or 10995.
Like Doanh nhân số