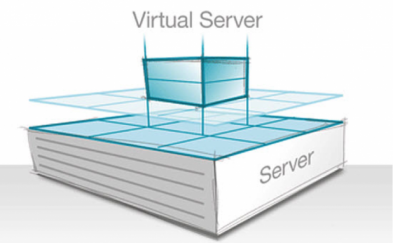
024 38560777
Integer (Kiểu số nguyên)
Trong toán học, số nguyên bao gồm các số tự nhiên dương (1, 2, 3, …), các số đối của chúng (−1, −2, −3, ...) và số không. Phát biểu một cách hình thức như sau: các số nguyên là miền xác định nguyên duy nhất mà các phần tử dương của nó được sắp thứ tự tốt (well-ordered), và các thứ tự đó được bảo toàn dưới phép cộng. Cũng như số tự nhiên, các số nguyên hợp thành một tập vô hạn đếm được (Xem thêm: Phép chứng minh tập hợp số nguyên là đếm được). Trong toán học, tập hợp gồm tất cả các số nguyên thường được ký hiệu bằng chữ Z in đậm, (hoặc \mathbb{Z}), đó là viết tắt của Zahlen (có nghĩa "số" trong tiếng Đức).
By English
An integer is a number that can be written without a fractional or decimal component. For example, 21, 4, and −2048 are integers; 9.75, 5½, and √2 are not integers. The set of integers is a subset of the real numbers, and consists of the natural numbers (1, 2, 3, ...), zero (0) and the negatives of the natural numbers (−1, −2, −3, ...).
The name derives from the Latin integer (meaning literally "untouched," hence "whole": the word entire comes from the same origin, but via French). The set of all integers is often denoted by a boldface Z (or blackboard bold \mathbb{Z}, Unicode U+2124 ℤ), which stands for Zahlen (German for numbers, pronounced [ˈtsaːlən]).
The integers (with addition as operation) form the smallest group containing the additive monoid of the natural numbers. Like the natural numbers, the integers form a countably infinite set. In algebraic number theory, these commonly understood integers, embedded in the field of rational numbers, are referred to as rational integers to distinguish them from the more broadly defined algebraic integers.
The integers (with addition and multiplication addition) form a unital ring which is the most basic one, in the following sense: for any unital ring, there is a unique ring homomorphism from the integers into this ring. This universal property characterize the integers.
Like Doanh nhân số